If you’re surrounded by clowns, chances are good you climbed into a clown car.
Between Rationalism and Fanaticism

In my opinion what makes Thelema distinctive is not the occultism, not the ontology, not the ethics, not the individualism. It’s that he took the western occult tradition with its God as a creative artist and inflected it through a Nietzschean understanding of life.
Renaissance occultism is based upon a view of the cosmos where everything is ordered into spheres or levels with Earth as the focus. Natural magic is about drawing power or spiritus down from higher spheres into lower ones. “Cabalistic” magic is about ascending to superluminary spheres and mastering the angelic forces there—which tips over very easily into mysticism, as it does in Thelema. In short it’s based on a hierarchical, anthropocentric view of the universe as a kind of container focused on human affairs, and the container is overall not that large.
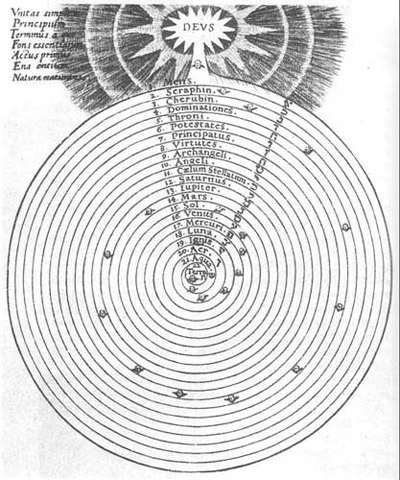
This view was largely replaced by the natural philosophy in the 17th and 18th centuries. According to this new view, the universe does not behave according to purposes but rather mechanisms. There are no “pulls” in the universe, only “pushes”. And the universe in which these abstract mathematical laws operate is vast enough to overwhelm the imagination and the human perspective all together. The picture of the universe generated by this natural philosophy ultimately left up in the air the place of humans in it. And with this disenchanted view of nature came a challenge to both religion and magic.
Rather than recoiling from this picture of nature into a kind of reenchanted fantasy about life, Crowley instead embraces it. The sheer enormity of the cosmos is one of the premises of Crowley’s view of reality, embodied in the goddess Nuit. The pure mathematical view of reality is not rejected either but embraced. Mathematics was part of occultism going back at least to Pico, but Crowley really makes it one of the main themes of his spirituality. So in other words rather than trying to hide from the implications of modernism, Crowley leans into them.
And he understands the fundamental spiritual problem in a very modernist way. The problem we face is not suffering, and it’s not ethics. These are pre-modern or early modern ways of looking at the problem. No, the main problem is meaning. It’s the senselessness of the world. Crowley was motivated by this experience of senselessness at least since he was a student at Cambridge, and he writes about it at least as late as Little Essays Toward Truth.
What then determines Tiphareth, the Human Will, to aspire to comprehend Neschamah, to submit itself to the divine Will of Chiah?
Aleister Crowley, Little Essays toward Truth, “Man”
Nothing but the realisation, born sooner or later of agonising experience, that its whole relation through Ruach and Nephesch with Matter, i.e., with the Universe, is, and must be, only painful. The senselessness of the whole procedure sickens it. It begins to seek for some menstruum in which the Universe may become intelligible, useful and enjoyable. In Qabalistic language, it aspires to Neschamah.
The way he understands a possible solution to senselessness is very modernist as well. The solution cannot be sought in reason. Reason operates according to the principle of sufficient reason, i.e., for any proposition F, there must be a ground G for it, or for any event B, there must be a sufficient explanation A. Putting the principle of sufficient reason at the center of human relating to the world is what generated the picture of a senseless, purely mechanical world in the first place. Therefore, reason—specifically the application of the principle of sufficient reason—must be limited, but to limit reason it must be transcended.
But—the transcendence of reason cannot interfere with the legitimate operation of reason within its own domain. Crowley is not looking to reenchant nature in some naive way. He accepts the findings of the scientific view of reality and even holds them to be axiomatic for his spirituality. Nor can the transcendence of reason be a mere animalistic “overcoming” of reason. One cannot simply will oneself to be irrational, for instance. Both of these avenues would represent a kind of fanaticism.
So Crowley has to manuever somehow between the Scylla of rationalism on the one hand and the Charybdis of dogmatism or fanaticism on the other.
This is a very modernist—specifically German Idealist—way of looking at things. When a person with a background in the philosophy of Kant, Fichte, Hegel, and Nietzsche hears Crowley talking about transcending “because,” they’re hearing a tune they could hum in their sleep.
And Crowley’s proposed solution to this problem is will. Will transcends reason. You cannot ask “why” of will. In and of itself it prevents the questioning but instead gives orders. It’s authoritative. This is how he avoids rationalism.
But will also represents the “true” self of the individual. It is not a mere replacement for Jehovah. It is not a projection of the law of the father. Nor is it exactly bodily or animal instinct. This is how Crowley avoids fanaticism.
The ground of the distinction between the finite will and the infinite will
 1. “[Hadit] hath no Nature of His own, for He is that to which all Events occur.” (Djeridensis Comment on AL II.2)
1. “[Hadit] hath no Nature of His own, for He is that to which all Events occur.” (Djeridensis Comment on AL II.2)
2. The nature of something is its characteristic behavior, the way it tends to act.
3. Actions are intelligible in terms of their ends. Running and cooking are differentiated by the results they tend to realize. (It’s not necessary for the result to be separate from the doing. Consider the action “standing up.”)
4. Having no nature, Hadit has no characteristic end. (“For pure will, unassuaged of purpose, delivered from the lust of result, is every way perfect.” AL II.44)
5. But Hadit is not for that reason without activity. (“‘Come unto me’ is a foolish word: for it is I that go.” AL II.7)
6. Hadit is pure going—action done for its own sake. This is the same thing as Hadit having Nuit for his end. “But to love me is better than all things” (AL I.61) “Now Hadit knows Nuit by virtue of his ‘Going’ or ‘Love.’ It is therefore wrong to worship Hadit; one is to be Hadit, and worship Her.” (New Comment to AL II.8)
7. Hadit is the true self of the aspirant. (“Thou who art I beyond all I am, who hast no nature and no name…” Liber XV)
8. The activity of the true self is the true will. (“…the Adept will be free to concentrate his deepest self, that part of him which unconsciously orders his true Will…” Liber Samekh)
9. My true will being infinite—having no goal other than Nuit—it cannot be captured by any finite expression, not even a single word.
10. This is the ground for the distinction between finite will and infinite will which Crowley makes in Liber CL: “And to each will come the knowledge of his finite will, whereby one is a poet, one prophet, one worker in steel, another in jade. But also to each be the knowledge of his infinite Will, his destiny to perform the Great Work, the realization of his True Self.”
11. But the distinction between the finite will and the infinite will is a distinction of thought, not a real distinction. In other words, the difference between the infinite will and the finite will is a difference made only by the finite will. This is because the infinite will—almost by definition—can’t have anything to do with other than itself or its own pure activity.


